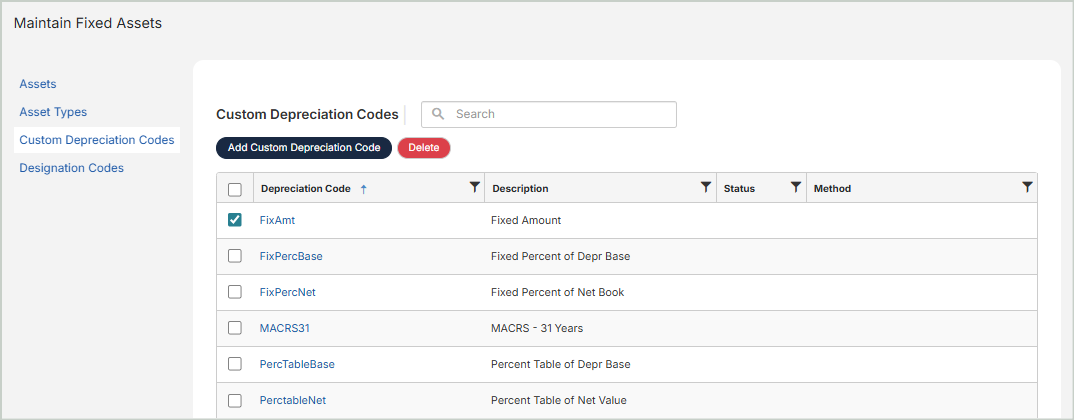
Custom Depreciation Codes
If you don't want to use the standard depreciation calculation methods built into the system, you can create your own depreciation codes with a non-standard calculation method. You’ll use these codes when assigning the depreciation method for an Asset Type ID (see Asset Types).
MIP provides the following standard depreciation calculation methods:
-
Straight Line
-
Sum of the Years Digits
-
150 Percent Declining Balance
-
200 Percent Declining Balance
-
No Depreciation Calculated
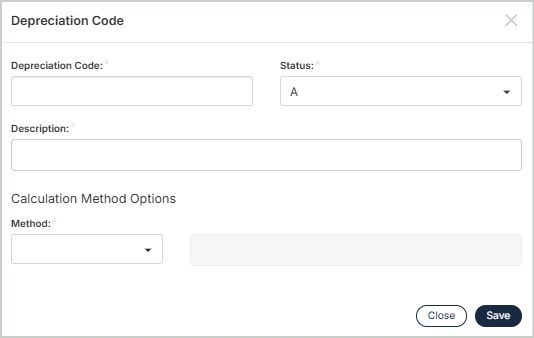
Add / Edit Custom Depreciation Codes
To create a new custom depreciation code, select Add Custom Depreciation Code.
To edit an existing depreciation code, select it from the grid.
Straight Line (SL): This is the simplest method of depreciation. It is calculated by taking the Cost minus the Salvage value, divided by the Useful Life of the asset. The depreciation expense is roughly the same amount for every frequency during the life of the asset. You may want to use this depreciation method when an asset's usefulness decreases evenly over the life of the asset. Straight Line is used as the Switch To Depreciation Code (Maintenance > Fixed Assets > Asset Types) when using an accelerated depreciation code.
Sum of the Years Digits (SYD): This method results in a decreasing depreciation charge based on a decreasing fraction of depreciable cost.
This is sometimes referred to as an accelerated depreciation method, because the depreciation expense is much higher in the beginning of the asset's life. You may want to use this depreciation method when the asset's usefulness decreases more rapidly at the beginning of the asset's life.
The fraction's denominator is calculated using the following formula:
(n(n+1))/2 = SYD denominator
"n" represents the number of years to be depreciated. If you want to depreciate something for 5 years, the SYD denominator would be 15. Therefore, the first year depreciation would be calculated using the remaining asset's life (in full years) of 5 years divided by the SYD of 15 (5/15=33.3333%). The second year is 5 years divided by 15 SYD equaling 26.6667%.
Declining Balance (DB150): This method is a decreasing charge method that uses 1 1/2 times the straight-line rate. This is sometimes referred to as an accelerated depreciation method because the depreciation expense is much higher in the beginning of the asset's life. You may want to use this depreciation method when the asset's usefulness decreases more rapidly at the beginning of the asset's life.
Declining Balance (DB200): This method is a decreasing charge method that uses 2 times the straight-line rate. This is sometimes referred to as an accelerated depreciation method because the depreciation expense is much higher in the beginning of the asset's life. You may want to use this depreciation method when the asset's usefulness decreases more rapidly at the beginning of the asset's life.
No Depreciation Calculated (NO): This method does not calculate any depreciation. If you select this method, you do not need to enter any information in the Expenditure or Accumulated Depreciation Account boxes when creating a new Asset Type on the Maintenance > Fixed Assets > Fixed Assets > Asset Types form.
Depreciation Code: Enter a unique ID for this depreciation code.
Status: Select a status from Active, Inactive, or Discontinued.
-
Set a depreciation code’s status to Active when you want to use it throughout the system. Active codes appear on reports.
-
Set a depreciation code’s status to Inactive when you don’t want to use it regularly, but may still need to use it at some point. A warning message will appear when you attempt to use inactive depreciation codes.
-
Set a depreciation code’s status to Discontinued when you no longer use it. Discontinued codes still appear on reports.
Description: Enter or change the description for the depreciation code.
Method: Select a non-standard depreciation method.
Fixed Amount (FA): Select this method to depreciate by an annual monetary amount.
Percentage of Depreciable Base (PD): Select this method to depreciate using a fixed percentage of the depreciable base (Cost minus Salvage value). This percentage is an annual amount.
Percentage of Net Book Value (PN): Select this method to depreciate using a fixed percentage of the Net Book Value (Cost minus Accumulated Depreciation). This amount is an annual amount.
Percentage Table of Depreciable Base (TD): Select this method to depreciate using variable percentages for each year of the depreciation. This calculation is based on the depreciable base (Cost minus Salvage). This amount is an annual amount.
Percentage Table of Net Book Value (TN): Select this method to depreciate using variable percentages for each year of the depreciation. This calculation is based on the Net Book Value (Cost minus Accumulated Depreciation). This amount is an annual amount.
Fixed Amount: Enter a value here to make an asset depreciate by a fixed amount.
Fixed Percentage: Enter a value here to make an asset depreciate by a fixed percentage.
Percentage Table: Enter yearly percentage depreciation values in this table. The sum of the percentages must equal 100%.
Note: You cannot set up a new custom depreciation code named MACRS (Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System) or ACRS (Accelerated Cost Recovery System). If you want to enter a depreciation code for a MACRS or ACRS-type asset, you can set up a custom depreciation code using one of the Percentage Table depreciation methods and use another name for the code, such as MACR31.
Once you're finished with your edits, Save your changes.
Delete Depreciation Codes
Before deleting a record, ensure you’ve selected the correct record you want to remove from the system. Deletion is permanent and cannot be undone.